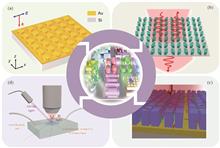
Bound states in the continuums (BICs) have attracted extensive attention in biological and chemical sensing. This is because they can significantly confine the light field and enhance light?matter interactions at the sub-wavelength scale. Currently, we have witnessed the emergence of several metaphotonic devices based on BICs. These devices are expected to break through the limitations of traditional biosensing in aspects such as miniaturization, specificity, and sensitivity. In this review, starting from BICs-based metaphotonic devices on different platforms, we systematically summarize the applications of metallic BICs, all-dielectric BICs, hybrid metal?dielectric BICs, and microfluidic BICs in biosensing fields, including refractive index sensing, surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy, and chiral sensing. Finally, we also explore the current limitations of BICs-based biosensor devices and discuss potential solutions to overcome these challenges in the future.
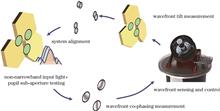
To achieve the integrated detection of large-aperture segmented optical systems and avoid the manufacture of equal-aperture detection devices, we propose a method of using a sparse aperture to construct an integrated detection device. By measuring the local wavefront at the seams and combining the wavefront reconstruction in the frequency domain, we can finally achieve the co-focus and co-phasing state testing of large-aperture segmented telescopes. Based on simulation analysis, the accuracy of the overall wavefront reconstruction (18 sub-mirrors) of our system is better than 0.01λ (λ stands for wavelength). Regarding the measurement and control accuracy of a single discrete aperture, on the basis of camera alignment, we conduct large-range feedback based on dispersion fringes and achieve precise co-phasing and accuracy verification based on the wide-band method. Ultimately, the closed-loop stabilization accuracy of the system in a non-vibration-isolated environment is better than 0.097λ. For spectral response testing, we use a split-type small-aperture integrating sphere to achieve a spectral splicing measurement of a large-aperture telescope. For an experimental system with an focal ratio of 10, the fluctuation of the light-intensity contrast in each field of view is better than 4%. Due to its small size and light weight, the proposed system can be used not only for integrated inspection in the manufacturing phase, but also for accuracy verification during on-site assembly and system calibration during operation intervals.
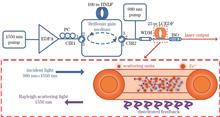
A Brillouin random fiber laser (BRFL) based on a low-concentration erbium-doped fiber is proposed as an active distributed feedback medium. Using a 980 nm pump source, a custom-made 25 m erbium-doped fiber with an ion mass fraction of 0.0035% serves as the Rayleigh scattering medium, providing distributed random feedback to achieve laser resonance. Compared to a traditional 20 km single-mode fiber (SMF), the erbium-doped fiber significantly enhances the distributed Rayleigh scattering intensity by approximately two orders of magnitude. This compact BRFL, leveraging the low-concentration erbium-doped fiber, demonstrates excellent laser noise suppression and frequency stability. Experimental results indicate that the proposed BRFL reduces relative intensity noise by about 20 dB and decreases frequency jitter over time by 64.3% compared to a BRFL using 20 km of SMF as the feedback medium. The active amplification of Rayleigh scattering in the erbium-doped fiber introduces optically controllable disorder, enabling the BRFL photonic system to display manipulated statistical properties of the dynamic spin glass phase. Moreover, the experimental observation of optically controlled replica symmetry breaking offers new avenues for exploring laser physics and nonlinear phenomena.
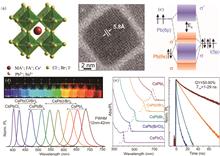
Superfluorescence is a transient and intense coherent light generated by the cooperative spontaneous emission of multi-body particles, which has significant application potential in quantum information technology, quantum computing, and multi-entangled quantum light sources. In recent years, perovskite quantum dot superlattices, with their unique structures and excellent optical properties, have become an ideal platform for studying superfluorescence. In this paper, we review the assembly and preparation techniques of perovskite quantum dot superlattices, explore the latest research progress in related fields, and summarize the research achievements of superfluorescence based on this system. Finally, we look ahead to the development prospects of superfluorescence in the perovskite quantum dot superlattice system.
We report an orthogonally polarized dual-frequency continuous-wave (CW) Er∶?YAG laser that can simultaneously output laser with wavelengths of 1617 nm and 1645 nm. Polarization beam splitter (PBS) prism and etalons are inserted into the cavity to generate an orthogonally polarized dual-frequency mode. The maximum output power of the S-polarized 1645 nm and the P-polarized 1617 nm lasers is 1.074 W and 0.242 W, respectively. We measure the longitudinal mode spectrum of the output laser using a Fabry?Perot (FP) interferometer and prove that the lasers at both wavelengths are single longitudinal mode. The M2 factors of the 1617 nm and 1645 nm lasers are 1.32 and 1.87 in the x direction and 1.38 and 2.06 in the y direction, respectively, and the frequency difference is 3.28 THz.
We propose an ultra-wideband reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) based on a dual-wing grooved symmetric structure. In our design, the grooves on both sides of the unit cell can effectively extend the current path and significantly improve the unit's broadband characteristics. We couple it with a high-precision voltage-controlled driver circuit, and the proposed RIS can adjust the unit's electromagnetic response based on theoretical coding in real time, thus achieving precise electromagnetic wave control. Through our experiments, we find that the RIS achieves a 1 bit phase tuning range from 7.3 GHz to 13.9 GHz, with a relative bandwidth of 62.3%, covering the C, X, and Ku bands. Moreover, the RIS achieves radar cross section (RCS) reduction of more than 10 dB in the range of 7?14 GHz, and the reduction can reach up to 15 dB in most frequency bands, with the maximum reduction being 40 dB. Additionally, our experimental verification also confirms the RIS's capability to manipulate single beams, asymmetric dual beams, and multiple beams, which provides an important reference for the multi-band cooperative applications of RIS.
Optical vortices have demonstrated significant potential in diverse applications, including particle micromanipulation, optical communication, and optical imaging. Among these, the generalized perfect optical vortex (GPOV) has emerged as a focal area of research due to its highly customizable intensity profiles and beam radius that remain independent of topological charges. These attributes have established GPOV as a versatile tool in advanced optical micromanipulation. In this paper, we employ blazed grating technology to enhance the generation of GPOV and integrate them into manipulation experiments involving polystyrene fluorescent microspheres. Through theoretical and experimental validation, we demonstrate the feasibility and precision of transporting particles along customizable paths. This research advances the integration of light field modulation and optical micromanipulation, paving the way for potential applications in microscale delivery systems.
Multiple-resonance thermally activated delayed fluorescence (MR-TADF) materials have advantages such as narrowband emission, small singlet-triplet energy level differences, and large molar extinction coefficients. These characteristics enable a combination of high efficiency and high color purity, granting these materials significant application potential in ultra-high-definition displays. Consequently, they have gained widespread attention. Since the first MR-TADF material was reported in 2016, this field has witnessed rapid advancements. However, blue MR-TADF materials with higher energy levels often suffer from poor carrier injection and transport capabilities, limiting their performance in terms of efficiency and color purity. MR-TADF materials with multi-boron structures, owing to their multiple electron-deficient boron atoms, enhance electronic delocalization and molecular orbital overlap and coupling. This suppresses non-radiative transitions and improves emission efficiency. Moreover, the increased molecular rigidity and multi-resonance effects reduce vibrational and rotational energy level distributions in the excited state, resulting in narrower full width at half maximum (FWHM) emissions. Consequently, these materials have emerged as a prominent choice for constructing deep blue organic emissive materials, driving significant progress in this field. In this paper, we comprehensively explore recent advances in blue MR-TADF materials with multi-boron structures, focusing on molecular design, photophysical properties, and optoelectronic performance in organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs). By clarifying the relationship between molecular structure and performance, we aim to provide valuable guidance for future research. Finally, we present perspectives on the future development of blue boron-containing MR-TADF materials.
In recent years, with the widespread application of laser processing technology in micro-nano scale materials and devices, research into characterization techniques for laser processing has played a crucial role in understanding laser-material interactions, optimizing the processing process, and improving processing quality. These techniques have found broad applications in fields such as micro-nano optoelectronic device fabrication and biomedical material processing. However, as processing precision improves and application areas expand, performing in-situ rapid and real-time characterization of laser-processed micro-nano structures has become a key technical challenge. We introduce the major in-situ characterization techniques currently used in laser micro-nano processing, classifying them into two categories: geometric in-situ characterization and ultra-high spatiotemporal resolution in-situ characterization. Geometric in-situ characterization, including techniques such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and structured light three-dimensional imaging, is widely employed for high-resolution imaging of surface morphology, enabling rapid in-situ characterization of laser-processed micro-nano structures. Ultra-high spatiotemporal resolution in-situ characterization techniques, such as pump?probe imaging and single-pulse ultrafast imaging, allow observation of the transient evolution of materials during laser processing with picosecond to femtosecond temporal resolution. These techniques reveal changes in microstructure and material properties, providing crucial insights into the interaction between lasers and materials. Finally, we summarize the findings and present an outlook on the future development of in-situ characterization technologies for laser processing.
We propose a hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas sensor based on ZnO-CuO composites modified with a single-mode fiber. Copper (Cu) is doped into ZIF-8 and annealed at high temperatures to form a ZnO-CuO composite structure. This composite is then coated onto a single-mode fiber, which has been pre-coated with a thin gold nanoparticle film using the lift-off method. This sensor employs a multimode fiber‒single-mode fiber‒multimode fiber (MMF‒SMF‒MMF) sensing structure that exploits the localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) effect generated by the gold nanoparticle film. Due to the specific adsorption of hydrogen sulfide by ZnO-CuO, changes in the spectral wavelength can be used to detect H2S volume fractions. ZnO-CuO powder is prepared by adding copper chloride dihydrate at mass ratios of 20%, 40%, and 60% relative to ZIF-8, resulting in three sensors: ZnO-CuO-20, ZnO-CuO-40, and ZnO-CuO-60. The experimental results indicate that, under ambient conditions of 25 °C and 30% relative humidity, the ZnO-CuO-40 sensor exhibits the best performance. In the 1×10-6‒7×10-6 volume fraction range, a redshift in the resonance wavelength occurs as the hydrogen sulfide volume fraction increases, with a wavelength drift of 1.133 nm. The sensitivity is 188.82 pm/10-6, the detection limit is 969.3089×10-12, and the response time is approximately 125 s. This sensor demonstrates excellent temporal stability and high selectivity for hydrogen sulfide detection.
Weyl points, as a key concept in topological photonics and condensed matter physics, have seen significant advancements in both theoretical and experimental research in recent years. As singularities of Berry curvature, the emergence of Weyl points is always associated with the construction of topologically nontrivial systems, thus attracting considerable attention. Moreover, the presence of open Fermi arc surface states at the interface provides new insights into the manipulation of electromagnetic fields. However, realizing Weyl points requires the breaking of time-reversal symmetry or space inversion symmetry, which makes naturally occurring Weyl semimetals rare. Due to their high degree of freedom and customizable band structure, metamaterials are well-suited for constructing systems with Weyl points. We focus on the experimental characterization of electromagnetic Weyl points, particularly summarizing common configurations of Weyl metamaterials that break space inversion symmetry. We also analyze commonly used experimental measurement methods for Weyl points and introduce the experimental manifestations of Fermi arcs as typical observable phenomena. Based on this, we explore the potential applications of electromagnetic Weyl metamaterials in multiple fields.
With the rapid advancement of modern information technology, there is an urgent need to enhance multiple targets and multiple tasks detection capabilities in complex environments. Traditional light detectors primarily capture scalar parameters such as light intensity, whereas light in free space inherently carries rich, multi-dimensional information such as polarization, spectral data, and phase angle those are often interrelated and overlapping. This presents significant challenges in simultaneously and independently extracting multiple dimensions of information. Emerging multi-dimensional detectors are positioned to overcome these challenges by simultaneously acquiring and integrating complex multi-dimensional data, which is crucial for the detection and identification of fast, weak, and small targets in extreme environments. In this paper, we focus on new detectors designed to capture parameters like intensity, phase angle, polarization, and spectrum, while also exploring the potential for multi-dimensional fusion detection, on-chip integration, and future trends in multi-dimensional sensing technology.
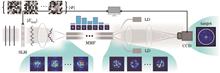
We propose a parallel generation method for multi-band linear frequency modulated (LFM) signals based on an extensible optical frequency operation module (OFOM). By replicating the second-stage spectral manipulation architecture, we achieve the parallel generation of multiple radar signals. Additionally, we discuss the optimization method for the output signal-to-clutter ratio (SCR) of OFOM. Compared to traditional methods for parallel multi-band signal generation, the proposed method not only simultaneously generates ultra-wideband dual-band signals but also allows for independent tuning of the generated signal parameters, while maintaining a simple and reliable system structure. In our experiments, we use this method to generate dual-band signals ranging from the very high frequency (VHF) band to the X-band, with bandwidths adjustable from 2.4 MHz to 6 GHz, and capable of producing large bandwidth signals of 1.2 GHz at low central frequencies. This technology holds potential applications in future radar systems, significantly enhancing system performance and expanding functionalities.
We use an ultra-short pulse laser to pump photonic crystal fiber. Benefiting from nonlinear effects such as four-wave mixing and fiber dispersion, we successfully generate an optical communication band ultra-strong photon correlation light field, characterized by a central wavelength of 1550 nm, a spectral width of 5 nm, and a second-order correlation function g(2)(0) is up to 774.2±6.0. Through the analysis of the statistical distribution of photon numbers and the second-order correlation function g(2)(0) for coherent light field, thermal light field, and photon correlation field as functions of the average photon number, we find that the ultra-strong photon correlation light field in the optical communication band exhibits a wide photon number distribution range and a higher second-order correlation function. The results indicate that by adjusting the pump power of the ultra-short pulse laser, we can transition the photon statistical properties of the emitted light field among coherent light field, thermal light field, and photon-correlated light field. The ultra-strong photon correlation light field generated by this method provides a novel technical approach for advancing research in quantum precision measurement and quantum computing.
In the post-Moore era, microelectronic systems characterized by miniaturization and integration and optoelectronic systems with the advantage of large transmission capacity are approaching their development limits. The silicon based optoelectronics (SBO) chip benefits from the mature CMOS technology and can integrate microelectronic and optoelectronic systems on a large scale on a silicon substrate. It is one of the best solutions to meet the development requirements of information systems in terms of miniaturization, functionality, large scale, and low power consumption. Based on the fundamental elements of information technology, our research briefly describes the development process of microelectronics and optoelectronics and demonstrates the necessity of SBO technology and its crucial enabling effect on the miniaturization of information systems. It further elaborates on some significant progress in recent years and analyzes three typical applications of SBO under the demand for large computing power, namely optical interconnection, optoelectronic sensing, and optoelectronic computing, so as to provide a valuable reference for researchers in related fields and promote the further exploration and application of SBO technology in the development of information technology.
The 3?5 μm mid-infrared band situated within the atmospheric transmission window and encompassing numerous absorption bands of gas molecules, has drawn extensive concern in the fields such as laser communication, biomedical, material processing, military confrontation, and aerospace. Among diverse types of lasers, fiber lasers stand out for their portability and stability, thus serving as an excellent laser light source. Mid-infrared fiber materials, such as fluoride glass, have the advantages of low phonon energy, high transmittance, high solubility of rare earth ions, and a wide transmission window, which can be used as gain materials for mid-infrared lasers. Fluoride glasses are classified into fluorozirconate, fluoroaluminate, and fluoroindate glasses. Mid-infrared glass fibers have achieved 4.3 μm fluorescence output, representing the longest wavelength mid-infrared fluorescence output obtained in fluoride fibers to date. This study reviews the current research and development of fluoride glass composition and glass structure, and focuses on introducing the fluoroaluminate, fluorozirconate, and fluoroindate glasses and fibers developed by our team, which have good stability and high laser damage threshold. It also reports the progress in mid-infrared laser output achieved by our team.
Fluorescence microscopy is a vital tool in biomedical research, enabling high-resolution imaging by using fluorescent dyes or proteins to label specific cells or molecules, which then emit fluorescence under a microscope. Light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) is an emerging three-dimensional imaging technology that achieves high-throughput, high-resolution 3D imaging by rapidly scanning thin samples. This technique offers advantages such as low phototoxicity and photobleaching, high photon efficiency, fast imaging speed, and high resolution. It is widely used in fields such as neuroscience, cell biology, and pathology. LSFM shows great potential in three-dimensional pathological analysis. Unlike traditional two-dimensional pathology slides, 3D pathological analysis provides complete spatial information on tissue structures, aiding in a more comprehensive understanding of disease mechanisms. The development of 3D pathological analysis significantly advances pathological research and clinical diagnostics, offering strong support for early disease detection, precise treatment, and personalized medicine. We first introduce the development of light-sheet microscopy and its applications in the pathological field, then discuss the main current approaches and methodologies for 3D pathological analysis. We focus on the potential applications of emerging multimodal large language models in pathological analysis.
We introduce a confocal functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) imaging system that utilizes a time-gated photon-counting technology. This innovative approach enables the acquisition of high sensitivity and high spatial resolution information within a confocal array while considering cost-effectiveness. The performance of the system is confirmed through a series of functional tests and phantom experiments. Results from these tests show that the system can freely set the position and width of the time gating window within a range of 0 to 10 ns, with a temporal resolution of 10 ps. Phantom experiment results indicate that the system achieves a quantitative ratio improvement of over 32.9% in the confocal array, an enhancement of more than 31.6% in the contrast-to-noise ratio, and an increase of over 29.5% in spatial fidelity. Therefore, the confocal fNIRS imaging system designed in this study, using time-gated photon-counting technology, effectively improves imaging quality at a reasonable cost. This provides instrumental support and methodological reference for related fNIRS research.
To improve the detection performance of glucose solutions, we first simulate and calculate the theoretical Raman spectrum of 99% (volume fraction) glucopyranose in the glucose solution. Next, we obtain experimental Raman spectra of glucose solutions at different mass concentrations using a Raman spectroscopy system. The theoretical calculations show that both types of glucopyranose exhibit characteristic peaks at 1125 cm-1, which is consistent with the experimental results. We then select the 1640 cm-1 characteristic peak of water as the internal standard peak for normalization. Finally, two quantitative analysis methods, the characteristic peak relative intensity method and the characteristic peak relative area method, are used for linear analysis. The linear correlation coefficient are 0.992 and 0.985, respectively. The lowest detection limits are 48.1 mg/dL and 52.3 mg/dL, and the lowest detection mass concentrations are all 12.5 mg/dL. The results indicate that the relative intensity method is simple and convenient, and provides a higher linear fitting, making it more suitable for accurate quantitative analysis of low mass concentration glucose solutions.
In recent years, researchers have integrated various detection mechanisms and investigated a series of optoelectronic detection technologies, aiming at online monitoring of hydrogen leakage in sealed hydrogen storage devices and hydrogen pipelines. This review categorizes direct and indirect detection methods and introduces recent advancements in detection technologies for hydrogen storage and transportation infrastructures. We conduct a comparative analysis to summarize the features and merits of each technology. Finally, we predict the prospects for the further development of optoelectronic detection technologies for the safe operation and maintenance of hydrogen storage and transportation systems.
In a levitated optomechanical system, the electric charge on the captured particle affects the sensitivity of measurements for force, gravity, acceleration, mass, and electric field. In this study, we propose and design a dual-beam optical trap chip with integrated electrodes to measure the charge on trapped particles using both direct current signal-driven electric fields and alternating current signal-driven electric fields. We successfully measure the precise charge of 10 μm diameter silicon dioxide microspheres trapped in the chip using an all-fiber miniaturized system. The results show that both methods yield a charge number of 493 for the silicon dioxide microspheres, confirming the reliability of these charge measurement methods.
Hydrogen energy, recognized as a clean and renewable source, has progressed rapidly in recent years under the global initiative for energy conservation and emission reduction. Optical sensing has also advanced swiftly, offering high precision, fast response, low power consumption, and no arc generation issues. It has been widely applied in remote sensing, bio-detection, agriculture, and environmental monitoring. Our study focuses on optical hydrogen sensing technology. We begin by briefly elucidating the principal features of optical hydrogen sensing compared to other hydrogen sensing technologies. We then review the different mechanisms and device types within existing optical hydrogen sensing technologies. Subsequently, we analyze and discuss the developmental history, current research status, and prospects of various optical hydrogen sensing types, including spectroscopy, palladium-hydrogen phase change, optical fiber, and photo-electric composite types, as well as the challenges they face. We also explore the application requirements for different scenarios. Finally, we compare the main technical performance indicators of mainstream optical hydrogen sensors that have been reported and provide perspectives on the research directions and future development of optical hydrogen sensing technologies.
To achieve higher accuracy in distortion correction with a limited number of marking points, we propose a method for optimal arrangement of marking points and reverse fitting distortion correction based on Zernike polynomials. In this method, we do not directly obtain the distortion distribution by fitting the position errors of marking points in the measurement results. Instead, we first fit the distortion errors based on the true positions of the components and then recover the distortion distribution through a reverse solution, which effectively avoids high-order errors introduced by the distortion itself. Additionally, we establish an algorithm for solving the marking point distribution by minimizing the matrix condition number and obtain the optimal arrangement coordinates for marking points based on Zernike polynomials. Compared with traditional methods, our proposed method improves the correction accuracy by more than 7 times with fewer marking points. This method has been successfully applied in the testing and processing of a Φ150 mm double-curvature elliptical mirror (asphericity of 8.86 mm, maximum distortion of 79 mm), achieving an average correction accuracy of 0.252 mm. The final surface accuracy, represented by the root mean square (RMS) error, reaches 0.029λ, which strongly supports the manufacturing of important optical components.
The event camera is a biomimetic dynamic vision sensor with advantages such as high time resolution, wide dynamic response range, and low power consumption. It can continuously capture changes in light intensity within the field of view. Developing visual measurement solutions based on event cameras is crucial for addressing dynamic problems. However, event-based measurement systems face two significant challenges. Firstly, event cameras output asynchronous event streams, which lose spatial information during transmission, making it difficult to reference traditional vision measurement algorithms. Secondly, event cameras lack reliable filtering algorithms, leading to poor-quality restored event frames, which are insufficient for reliably calculating image features. Our study outlines the development process of event cameras and reviews research on event-based target tracking. We also discuss advancements in event camera calibration, event-based structured light measurement, and event-based autofocus techniques. The 3D measurement scheme based on event cameras encounters issues with the unreliability of event stream data features and low measurement accuracy. By studying spatio-temporal information extraction algorithms, we aim to improve measurement accuracy. Developing high-speed event camera measurement systems and designing efficient solutions with low-bandwidth, low-power, and small computation will further advance the field of high-speed visual measurement.
Since the inception of holographic technology, its application value has been widely recognized. Among its applications, holographic optical elements have become important optical devices in various research fields due to their compact size, lightweight, and ease of fabrication. As an advanced theory of traditional holography, polarization holography enhances the ability to control the light field by adding the dimension of polarization. Therefore, the holographic optical elements can more comprehensively manipulate the amplitude, phase, and polarization of the light field in the spatial domain. Starting with the principles of polarization holography, we introduce phenomena observable through polarization holography, such as faithful reproduction and zero-order reproduction, which are not seen in traditional holography. Based on these phenomena, we elaborate on the research progress of polarization holography in the fabrication of various light field manipulation and detection devices. Finally, we analyze and forecast the future development trends of polarization holography technology, highlighting key scientific issues worthy of further attention and research.
The squeezing direction of the quadrature squeezed state is highly compatible with the quadrature amplitude modulation in classical communication, making the quantum communication protocol based on the quadrature squeezed state easier to implement and commercialize. Here, we experimentally prepare a 200 MHz broadband quadrature squeezed state corresponding to the optical fiber communication window. First, we construct an optical parametric amplifier with a cavity length of 8 mm and a full width at a half maximum of 210 MHz. Then, we develop a 1‒300 MHz low-noise balanced homodyne detector with a common-mode rejection ratio of up to 50 dB. Finally, we obtain a quadrature amplitude squeezed state with a bandwidth of 200 MHz at a wavelength of 1.3 μm, providing the necessary quantum light source for high-speed quantum communication.
We introduce a unique type of partially coherent light (PCL) that simultaneously carries a vortex phase and exhibits a special spatial correlation structure, known as radially polarized multi-Gaussian Schell-model fractional vortex (RP-MGSM-FV) beams. We outline the fundamental requirements for generating such light beams and derive the analytical expression for their cross-spectral density matrix after transmission through ABCD optical systems. We further examine the influence of the topological charge magnitude, sign, and coherence width of its vortex phase component on the intensity distribution at the focal plane. The results indicate that as the coherence width increases, the intensity distribution at the focal plane translates from a flat-top to a Gaussian-like shape, then to a flat-top, and ultimately to a ring pattern. An increase in the topological charge numbers leads to a distinct separation in the spatial distribution of the beam at the focal plane. Additionally, changes in the sign of the topological charge cause an inversion in the spatial distribution pattern, allowing for the detection of both the magnitude and sign of the topological charge in RP-MGSM-FV beams. These findings are significantly valuable in applications such as free-space optical communications and particle trapping in micro domains.
Stable time and frequency transfer is one of the two core technologies in time and frequency infrastructure systems. Optical fiber enables high precision and long-distance transfer, making it the best choice for terrestrial time and frequency transfer. In this study, we introduce the principles of fiber-optic time and frequency transfer and elaborate on the phase noise compensation methods using optical frequency transfer as an example. Addressing the limitations of current time and frequency transfer equipment that uses discrete optoelectronic devices, we explore and study the design approaches for optoelectronic integrated chips and demonstrate the advantages of photonic integration. Finally, we review recent progress in fiber-optic time and frequency transfer globally and present prospects.
A few-mode erbium-doped fiber amplifier (FM-EDFA) is a key device for realizing long-haul and high-capacity mode-division multiplexing (MDM) transmission. However, different mode channels across a wide wavelength band generate both mode-dependent and wavelength-dependent gains, leading to differential mode gain (DMG) over the wavelength span. This severely constrains the capacity enhancement of MDM transmission systems. In this study, we provide a comprehensive review of recent progress in the gain regulation of FM-EDFA. We systematically discuss the generation mechanism of DMG and its optimization strategies. The performance of DMG under various regulation schemes is then presented. Finally, we explore the research challenges related to DMG equalization under conditions of higher mode counts and wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) transmission.
In this study, we conduct a thorough investigation into the focusing transmission characteristics of scalar and vector beams in atmospheric turbulence by combining theoretical derivations with angular spectrum simulations. We compare the focusing performance of typical scalar beams (Gaussian beam) and vector beams (lemon vector beam and radially polarized vector beam) under weak and strong turbulent conditions. Our research reveals that, whether it is in weak or strong turbulent conditions, the focused Gaussian beam exhibits the highest average peak power density and the smallest radius of 63.2% encircled energy at the focal plane. However, its scintillation index significantly exceeds that of the focused lemon vector beam.
Traditional optoelectronic imaging technology, based on the principle of direct visual representation, fundamentally involves the direct and uniform sampling and reproduction of two-dimensional light field intensity signals in spatial dimensions. However, constrained by the physical and technological limitations of optical imaging systems and optoelectronic detectors, it has become increasingly insufficient to meet the growing demands for high resolution, high sensitivity, and multidimensional high-speed imaging in many fields. Computational imaging tightly integrates optical control in the physical domain with information processing in the digital domain. It offers innovative solutions to overcome the limitations of traditional imaging technologies, becoming the future direction of advanced optical imaging. From the perspective of the imaging chain, the optical control methods of computational optical imaging can be categorized into illumination control, optical system control, object control, and detector control. We focus on detector control—by introducing encoding devices (such as displacers, masks, and spatial light modulators) at the focal plane of the image sensor at the end of the imaging chain to regulate the high-dimensional light field. Coupled with post-processing reconstruction algorithms, this approach enables the decoupling of intensity, phase, 3D structure, light field information, and spectrum, paving the way for high-performance optoelectronic imaging and detection. These methods have the potential to overcome the inherent bottlenecks of traditional optoelectronic imaging, such as limited imaging dimensions and single-mode imaging, providing new avenues for achieving high resolution, multidimensional, hyperspectral, miniaturized, and ultrafast imaging.
Based on flip-chip technology, we demonstrate hybrid integration of a 4×1 indium gallium arsenide/indium phosphide (InGaAs/InP) single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) array and a silicon photonic chip. When testing two SPADs in the 4×1 SPADs array simultaneously at 10 ℃, we achieve on-chip photon detection efficiency of 5%‒6% under a low bias voltage, with dark count rates of 1.6×10-5 counts/gate and 4.5×10-5 counts/gate, respectively. Increasing the bias voltage, the on-chip photon detection efficiency can be further increased to more than 10%. Furthermore, using the integrated SPAD array and silicon photonic beam splitter, we realize the measurement of Hong‒Ou‒Mandel (HOM) interference for weak coherent states, achieving a HOM interference fringe visibility of 45.0%±1.2%. This demonstrates the effectiveness of hybrid integration of the photon manipulation on the silicon photonic chip and the multi-channel single-photon detection of the integrated SPADs array. The hybrid integration provides a potential solution for achieving scalable photonic quantum information systems.